2025/10/2大约 6 分钟
图
1. 环检测法
2. 拓扑排序(中序遍历然后再倒过来就是拓扑排序)
3. 二分图
class Solution {
// 记录图是否符合二分图性质
private boolean ok = true;
// 记录图中节点的颜色,false 和 true 代表两种不同颜色
private boolean[] color;
// 记录图中节点是否被访问过
private boolean[] visited;
// 主函数,输入邻接表,判断是否是二分图
public boolean isBipartite(int[][] graph) {
int n = graph.length;
color = new boolean[n];
visited = new boolean[n];
// 因为图不一定是联通的,可能存在多个子图
// 所以要把每个节点都作为起点进行一次遍历
// 如果发现任何一个子图不是二分图,整幅图都不算二分图
for (int v = 0; v < n; v++) {
if (!visited[v]) {
traverse(graph, v);
}
}
return ok;
}
// DFS 遍历框架
private void traverse(int[][] graph, int v) {
// 如果已经确定不是二分图了,就不用浪费时间再递归遍历了
if (!ok) return;
visited[v] = true;
for (int w : graph[v]) {
if (!visited[w]) {
// 相邻节点 w 没有被访问过
// 那么应该给节点 w 涂上和节点 v 不同的颜色
color[w] = !color[v];
// 继续遍历 w
traverse(graph, w);
} else {
// 相邻节点 w 已经被访问过
// 根据 v 和 w 的颜色判断是否是二分图
if (color[w] == color[v]) {
// 若相同,则此图不是二分图
ok = false;
}
}
}
}
}4. 并查集
class UF {
int count;
int[] parent;
public UF(int n){
this.count = n;
parent = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n;i++){
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public void union(int p, int q){
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if(rootP == rootQ){
return;
}
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
count--;
}
public int find(int x){
if(parent[x] != x){
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
public boolean connected(int p , int q){
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
return rootP == rootQ;
}
public int count(){
return count;
}
}5. 最小生成树算法
生成树:就是在图中找一棵包含图中的所有节点的树
最小生成树:所有可能的生成树中,权重和最小的那棵生成树就叫「最小生成树」
什么情况下加入一条边会使得树变成图(生成环)?
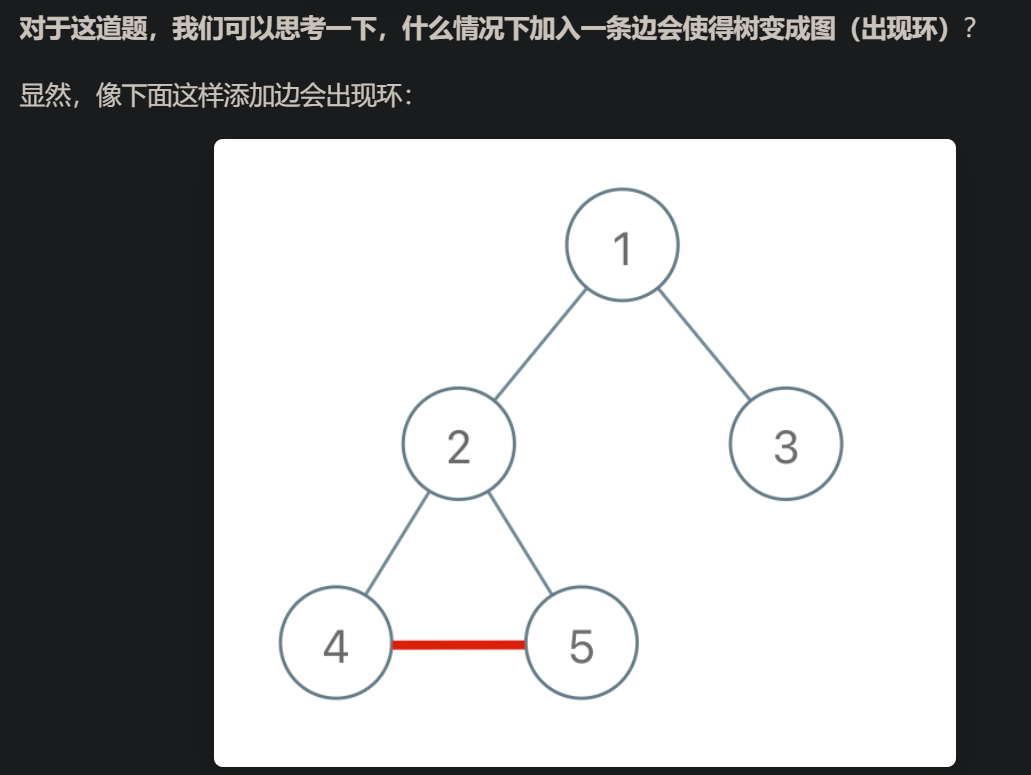
①Kruskal 算法
class Solution {
public boolean validTree(int n, int[][] edges) {
// 初始化 0...n-1 共 n 个节点
UF uf = new UF(n);
// 遍历所有边,将组成边的两个节点进行连接
for (int[] edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0];
int v = edge[1];
// 若两个节点已经在同一连通分量中,会产生环
if (uf.connected(u, v)) {
return false;
}
// 这条边不会产生环,可以是树的一部分
uf.union(u, v);
}
// 要保证最后只形成了一棵树,即只有一个连通分量
return uf.count() == 1;
}
class UF{
int count;
int[] parent;
public UF(int n ){
this.count = n;
parent = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n;i++){
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public void union(int p , int q){
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if(rootP == rootQ){
return;
}
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
count--;
}
public boolean connected(int p ,int q){
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
return rootP == rootQ;
}
public int find(int x){
if(parent[x] != x){
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
public int count(){
return count;
}
}class Solution {
public int minimumEffortPath(int[][] heights) {
int rows = heights.length;
int cols = heights[0].length;
UF uf = new UF(rows * cols);
List<int[]> edges = new LinkedList<>();
int[][] dircetion = new int[][] { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
int id = i * cols + j;
for (int[] d : dircetion) {
int ni = i + d[0], nj = j + d[1];
if (ni >= 0 && nj >= 0 && ni < rows && nj < cols) {
int nid = ni * cols + nj;
int diff = Math.abs(heights[i][j] - heights[ni][nj]);
edges.add(new int[] { id, nid, diff });
}
}
}
}
Collections.sort(edges, (a, b) -> (a[2] - b[2]));
for (int[] edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0];
int v = edge[1];
int weight = edge[2];
uf.union(u, v);
if (uf.connected(0, rows * cols - 1)) {
return weight;
}
}
return 0;
}
class UF {
int count;
int[] parent;
public UF(int n) {
this.count = n;
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) {
return;
}
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
count--;
}
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
return rootP == rootQ;
}
public int find(int x) {
if (parent[x] != x) {
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
public int count() {
return count;
}
}
}6. Dijkstra最短路径算法
Dijkstra 算法是一种用于计算图中单源最短路径的算法,本质上是一个经过特殊改造的 BFS 算法,改造点有两个:
1、使用 优先级队列,而不是普通队列进行 BFS 算法。
2、添加了一个备忘录,记录起点到每个可达节点的最短路径权重和。
Dijkstra 计算最短路径的正确性依赖一个前提:路径中每增加一条边,路径的总权重就会增加。然后你要求的是最小值
路径中每增加一条边,路径的总权重就会减少,然后你要求最大值,要是能够满足这个条件,也可以用 Dijkstra 算法。
伪代码逻辑
// 输入一幅图和一个起点 start,计算 start 到其他节点的最短距离
int[] dijkstra(int start, Graph graph) {
// 图中节点的个数
int V = graph.size();
// 记录最短路径的权重,你可以理解为 dp table
// 定义:distTo[i] 的值就是节点 start 到达节点 i 的最短路径权重
int[] distTo = new int[V];
// 求最小值,所以 dp table 初始化为正无穷
Arrays.fill(distTo, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// base case,start 到 start 的最短距离就是 0
distTo[start] = 0;
// 优先级队列,distFromStart 较小的排在前面
Queue<State> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> {
return a.distFromStart - b.distFromStart;
});
// 从起点 start 开始进行 BFS
pq.offer(new State(start, 0));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
State curState = pq.poll();
int curNodeID = curState.id;
int curDistFromStart = curState.distFromStart;
if (curDistFromStart > distTo[curNodeID]) {
// 已经有一条更短的路径到达 curNode 节点了
continue;
}
// 将 curNode 的相邻节点装入队列
for (int nextNodeID : graph.neighbors(curNodeID)) {
// 看看从 curNode 达到 nextNode 的距离是否会更短
int distToNextNode = distTo[curNodeID] + graph.weight(curNodeID, nextNodeID);
if (distTo[nextNodeID] > distToNextNode) {
// 更新 dp table
distTo[nextNodeID] = distToNextNode;
// 将这个节点以及距离放入队列
pq.offer(new State(nextNodeID, distToNextNode));
}
}
}
return distTo;
}Leetcode1514 无向图也能用,无向图相当于双向图
public double maxProbability(int n, int[][] edges, double[] succProb, int start_node, int end_node) {
List<double[]>[] graph = new LinkedList[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n;i++){
graph[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
for(int i = 0; i < edges.length;i++){
int from = edges[i][0];
int to = edges[i][1];
double weight = succProb[i];
graph[from].add(new double[]{(double)to,weight});
graph[to].add(new double[]{(double)from,weight});
}
return dijkstra(start_node,end_node,graph);
}
class State{
int id;
double distFromStart;
public State(int id, double distFromStart){
this.id = id;
this.distFromStart = distFromStart;
}
}
double dijkstra(int start, int end, List<double[]>[] graph) {
int n = graph.length;
double[] dist = new double[n];
Arrays.fill(dist, 0);
dist[start] = 1;
Queue<State> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> {
return Double.compare(b.distFromStart, a.distFromStart);
});
pq.offer(new State(start,1));
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
State cur = pq.poll();
int curId = cur.id;
double curDist = cur.distFromStart;
if(curId == end){
return curDist;
}
if(curDist < dist[curId]) continue;
for(double[] next : graph[curId]){
int nextId = (int)next[0];
double nextDist = dist[curId] * next[1];
if(nextDist > dist[nextId]){
dist[nextId] = nextDist;
pq.offer(new State(nextId,nextDist));
}
}
}
return 0.0;
}